Semiperfect-information Games Synthesis vs Estimator-based Synthesis
How are these two papers, Estimator-Based Reactive Synthesis and Semiperfect-information Games, related? (see also note 1 and note 2)
(we will look at them from the prospective of sure-winning objectives, thus no probabilities stuff)
Both papers aim at handling EXPTIME complexity of synthesis under partial information, and suggest PTIME algorithms. Are the ideas of how they handle partial information similar?
Recall that the estimator based synthesis consists of two steps: synthesis of positional estimators, and synthesis of the overall system. Partial information is handled in the synthesis of positional estimators. I think the main difference is in the way how winning-losing conditions are expressed, but the idea of the reduction to perfect information games is the same. The reduction idea can be summarized using the figure:
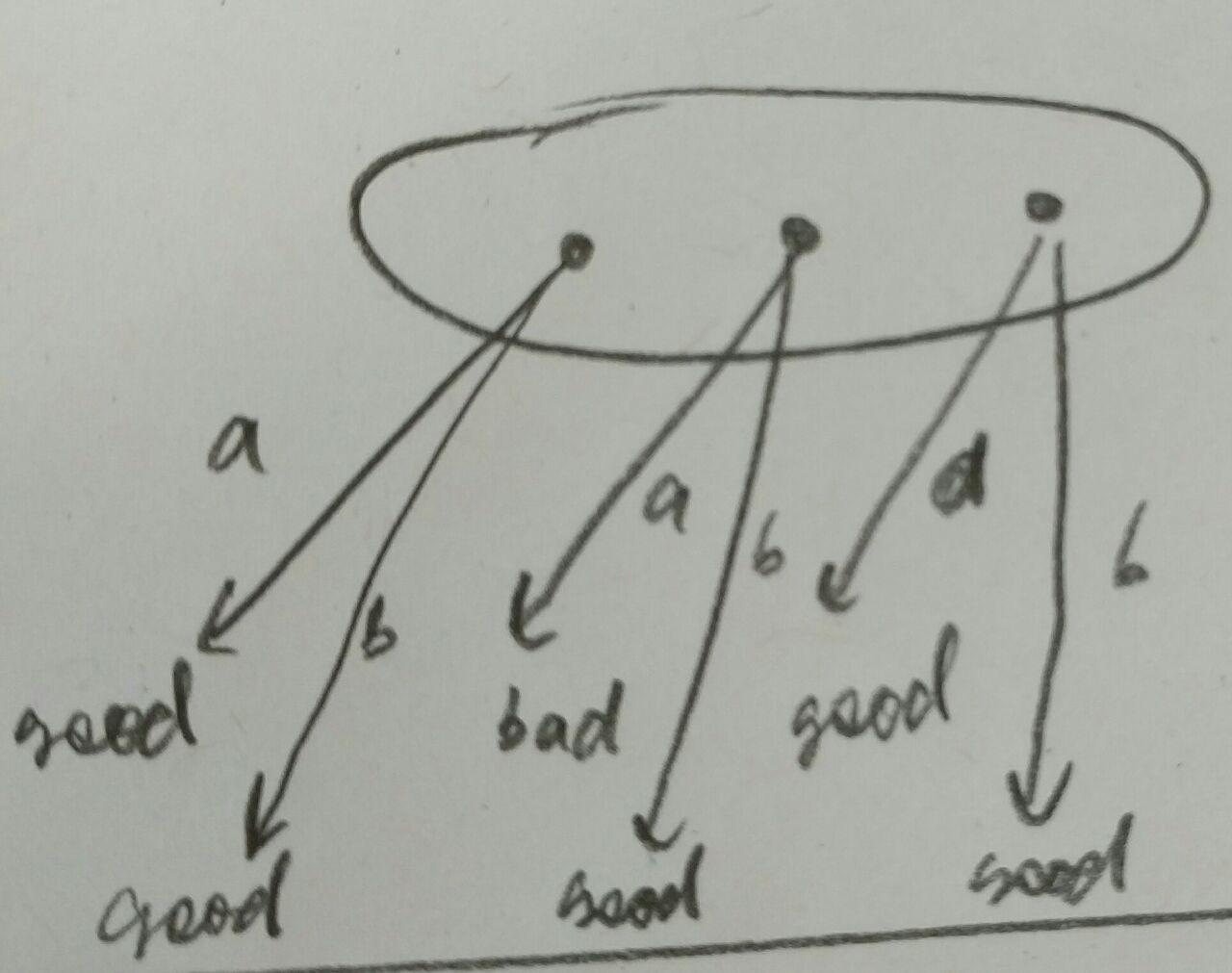
Imagine sys is in this big rounded state, but we don’t know in which state exactly. Then, one way to choose the move is to choose the move that works for every state. This simple idea might be overkill (if can learn that we cannot be in the middle state, for example), and it does not work for general imperfect games. But if consider special cases of imperfect information games, like the semiperfect-information games, or games used in the synthesis of estimators, then this simple idea works.
This idea can be also states as the reduction into perfect-information games, i.e., we can translate those special kinds of games into perfect information games without incurring exp blowup. We alredy did this for semiperfect games (note 2)), here is a very short illustration how to do this for games used to describe estimators:
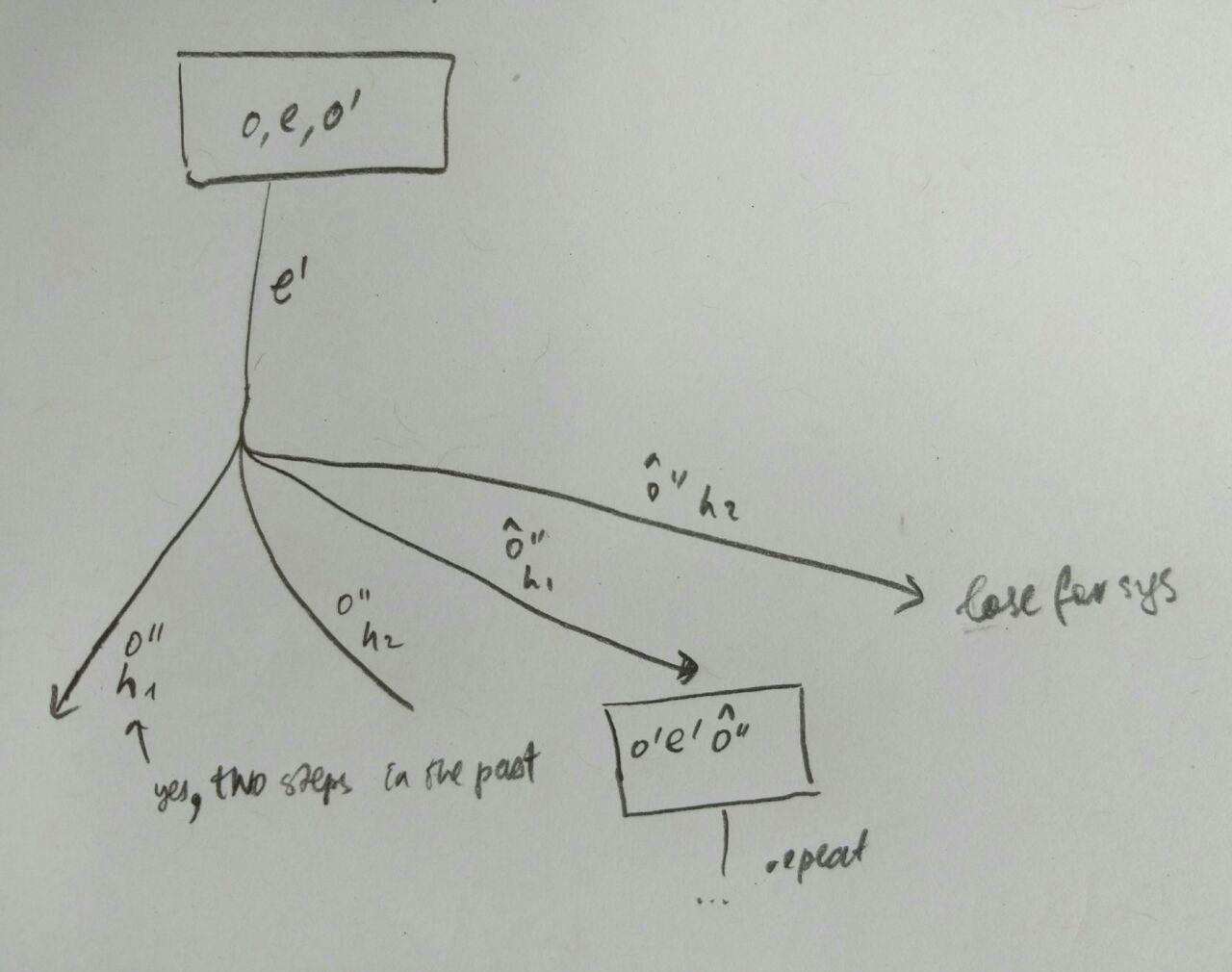
Estimator chooses $e$ (on the picture there is only one choice), then the environment chooses $o’’$ (visible inputs to the estimator) and $h$ (invisible (hidden) values two steps in the past). State is tuple $(o,e,o’)$ and consists of current value of inputs and estimations (outputs), and next inputs; state does not include hidden values. The estimator(sys) objective is to avoid going into losing states.