How does `smvtoaig` handle `LTLSPEC`?
LTLSPEC is translated into SMV module using ltl2smv.
(ltl2smv produces an SMV module for a given LTL property which describes
the transition relation of the automaton, and specifies accepting states
by marking them in JUSTICE.
ltl2smv introduces latches for states of the automaton,
and does not define APs of the automaton in any special way)
smvtoaig takes that SMV module and glues it with the rest.
To do so, the tool introduces AIGER_VALID which is true iff the transition
relation of the LTL module is true.
Thus, for every state of the automaton smvtoaig introduces one input and
one latch.
Environment provides the latch values for the next tick,
and AIGER_VALID tracks whether the latch values so far satisfied the
transition relation of the LTL automaton.
Also, smvtoaig shifts input signals by one tick (hm, why?).
AIGER_VALID tracks also whether we are in >0 tick now.
Additionally, there is input AIGER_NEXT_IGNORE_LTL that allows disabling
justice properties (i.e., the justice signals become false).
Note that there is an assumption on the environment which says
if it is false, AIGER_VALID also becomes false.
The justice signals are false if AIGER_VALID is false.
The variable AIGER_VALID is also referred to by AIGER_NEVER
when we generate output for safety properties.
Below is an example. The input was something like
MODULE main
LTLSPEC
! G F (some_input)
The output is below:
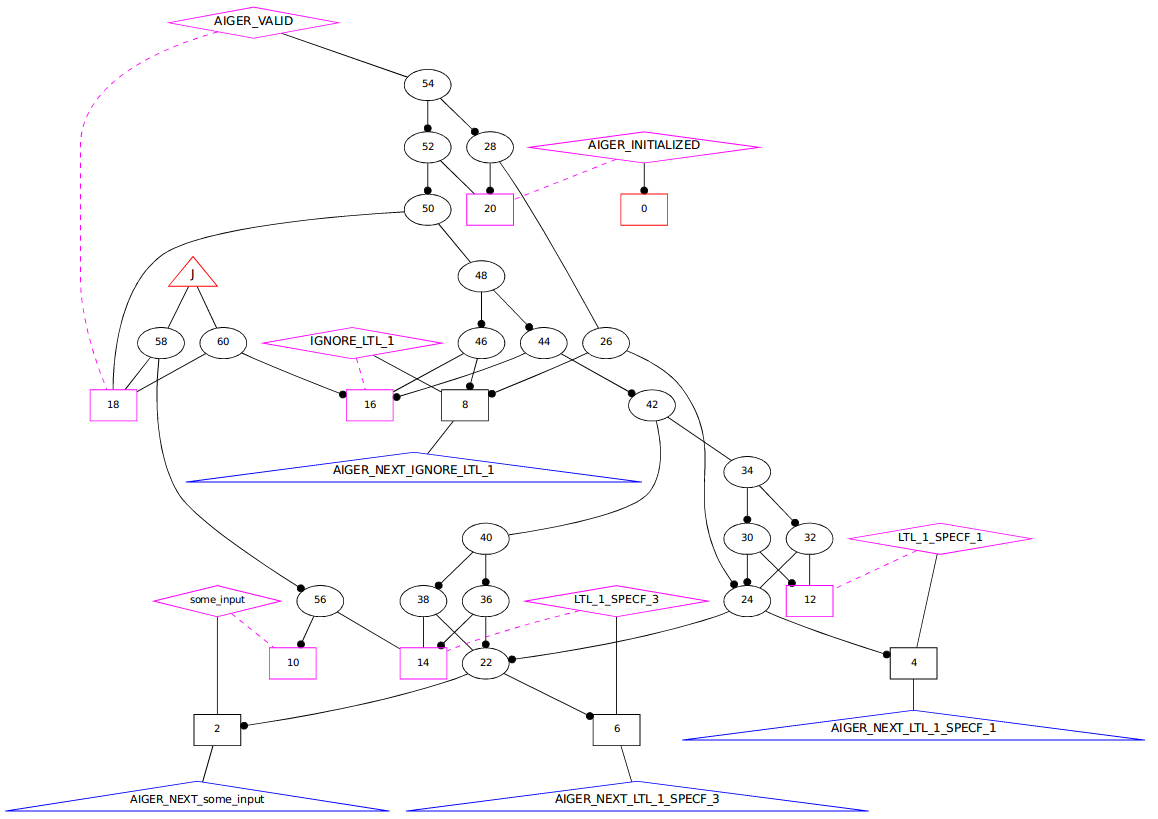
Some questions:
- why does
smvtoaigshift inputs by one tick? - why does
smvtoaigintroduce signalIGNORE_LTL? - why does
smvtoaigfor every input introduce one latch?
If you know a better description of how smvtoaig works – let me know!